Enterprise Guide to C2PA Watermarking AI Video Marketing: Content Credentials, DPDP/GDPR Alignment, and Ad Platform Compliance
Estimated reading time: 13 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Adopt a dual-layer approach that combines Content Credentials (C2PA manifests) with robust invisible watermarking for enterprise-grade provenance.
- Ensure DPDP and GDPR alignment with explicit consent, clear notices, and revocation workflows integrated into video rendering pipelines.
- Meet ad platform compliance by labeling synthetic media, surfacing provenance, and maintaining a “Provenance Pack” for audits.
- Deploy deepfake detection pre- and post-publish, and partner with trust labs for verified content certification.
- Operationalize at scale with reference architectures that embed manifests at render and preserve signals across storage, distribution, and governance.
C2PA watermarking AI video marketing represents the definitive 2026 standard for enterprise-grade synthetic media, integrating cryptographic provenance with robust visual and invisible identifiers to ensure brand safety. By operationalizing Content Credentials (C2PA manifests) and multi-layered watermarking, Legal, Compliance, and CISO teams can effectively mitigate deepfake risks while satisfying the stringent synthetic media disclosure India requirements. Platforms like TrueFan AI enable organizations to deploy these high-fidelity personalized campaigns at scale while maintaining an immutable audit trail of consent and content origin.
TL;DR: The 2026 Imperative for Legal and CISO Leaders
The regulatory landscape in 2026 mandates a shift from voluntary disclosure to technical enforcement of AI video compliance enterprise standards. With India’s Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act fully operational and MeitY’s 2025 explanatory notes requiring proactive labeling of synthetic content, enterprises must adopt a “provenance-by-design” architecture. This involves embedding C2PA manifests at the point of render, utilizing deepfake detection protocols for pre-distribution verification, and ensuring verified content certification across all ad platform compliance synthetic content checks. Failure to implement these cryptographic trust signals risks not only regulatory penalties but also immediate de-prioritization by major social media algorithms and ad exchanges.
1. Market Context: Why AI Video Provenance Enterprise Standards are Non-Negotiable
The concept of AI video provenance enterprise standards has evolved from a technical niche to a fundamental requirement for digital trust. In 2026, the ability to cryptographically prove the origin, toolchain, and edit history of a video asset is the only viable defense against the rising tide of sophisticated misinformation and brand impersonation.
India’s Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has accelerated this transition through a series of advisories and proposed amendments to the IT Rules. These mandates emphasize that intermediaries and content creators must provide clear, unambiguous labels for synthetically generated or significantly altered media. The 2025 policy trajectory suggests that “reasonable efforts” are no longer sufficient; instead, machine-readable metadata and persistent watermarking are becoming the baseline for legal safe harbor.
Simultaneously, global platforms have shifted their stance on synthetic media. YouTube and Meta now utilize automated audits to detect unlabeled AI content, often resulting in reduced reach or account suspension for non-compliant brands. Google’s expansion of SynthID across all modalities signals a future where “Captured with a camera” vs. “AI-generated” is a binary choice enforced at the hardware and software levels. For the enterprise, matching these trust practices is essential to avoid distribution friction and maintain brand safety AI watermarking integrity.
Source: MeitY Advisory on Synthetic Content (2024-2025)
Source: MediaNama YouTube AI Labeling Audit
Source: Google SynthID Expansion
2. Technical Foundations: Content Credentials Video Marketing and C2PA Manifests
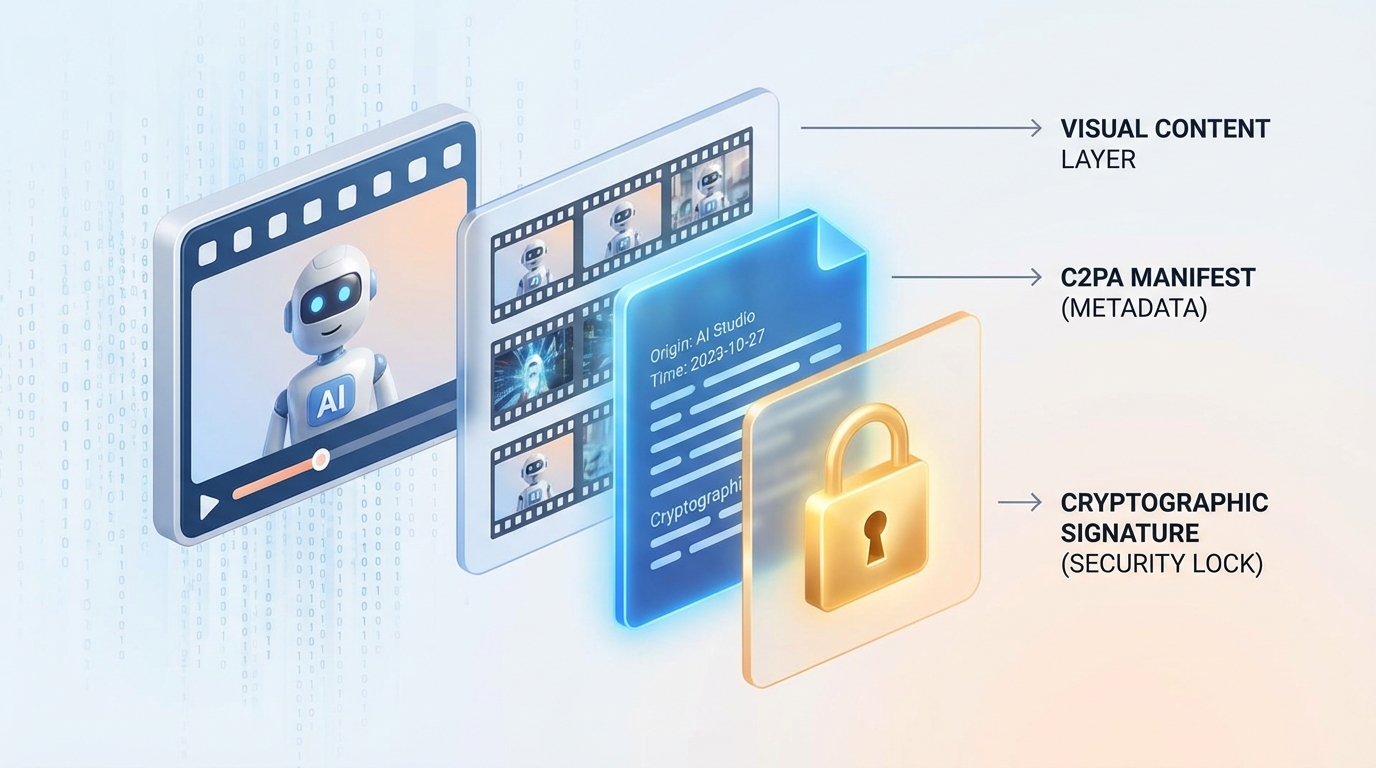
The implementation of content credentials video marketing relies on the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) standard. A C2PA manifest is a signed, tamper-evident record attached to a video asset that describes its lifecycle—from the initial generative model used to the specific edits made by marketing teams.
In a professional enterprise pipeline, these manifests act as a “digital nutrition label.” They provide assertions regarding the AI models employed, the identity of the signing entity, and the timestamp of creation. This cryptographic binding ensures that if the video is altered or stripped of its metadata, the discrepancy can be detected by C2PA-aware browsers and social platforms.
However, metadata alone is insufficient. The 2026 best practice combines C2PA manifests with resilient invisible watermarking at the render stage. While manifests provide the “soft binding” of data, invisible watermarks offer “hard binding” by embedding signals directly into the video frames and audio. This dual-layer approach ensures that provenance survives aggressive recompression, screen recording, and platform-specific processing. By achieving verified content certification through these combined methods, enterprises create a “trust surface” that is visible to both human viewers via UI badges and to automated crawlers via structured data.
Source: CSI Content Credentials Implementation
Source: AI Watermarking Market Growth
3. Compliance Deep-Dive: Synthetic Media Disclosure India and DPDP Act Integration
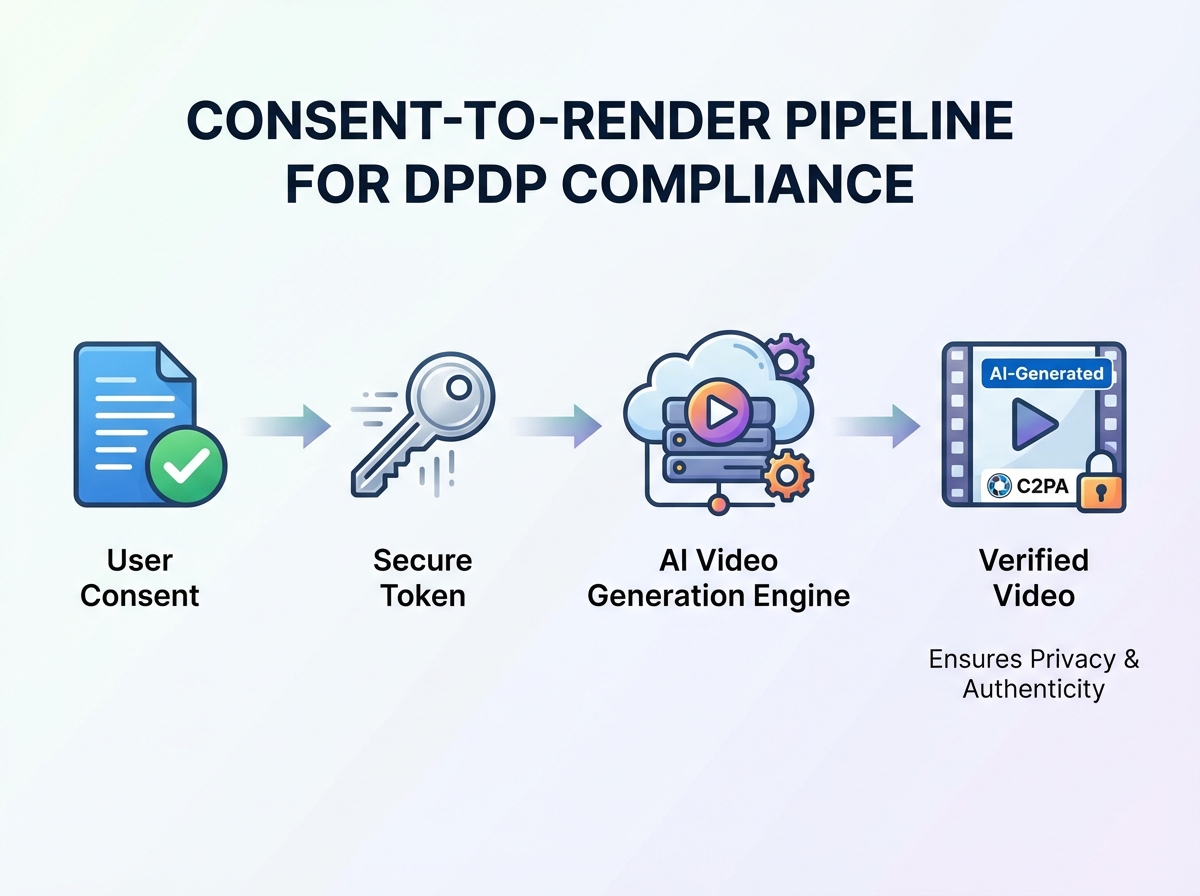
Navigating synthetic media disclosure India requires a nuanced understanding of both content labeling and data privacy. Under the DPDP Act, the use of personal data to generate personalized videos—such as a customer's name or purchase history—requires explicit, informed, and revocable consent.
DPDP Act consent management videos must be supported by a robust notice framework. Enterprises are required to provide clear notices in English and any of the Eighth Schedule languages relevant to the target audience. This notice must specify exactly how the data will be used (e.g., “to generate a personalized celebrity greeting”) and provide a simple mechanism for the user to withdraw consent. Operationally, this means the video rendering pipeline must be gated; if a user revokes consent, the system must automatically purge the personalization payload and halt any future re-renders of that specific variant.
Furthermore, celebrity avatar watermarking policies are critical for high-impact campaigns. These policies must include contractual clauses that mandate on-screen “AI-generated with consent” labels and C2PA assertions documenting the licensed use of the talent's likeness. This protects the brand from legal disputes and ensures that the synthetic representation of a celebrity is never mistaken for a live-action recording. By maintaining an audit trail of these approvals, enterprises can demonstrate compliance during regulatory inquiries or platform audits.
4. Global Operations: Ad Platform Compliance Synthetic Content and GDPR Alignment
For global enterprises, the challenge is to maintain ad platform compliance synthetic content standards across varying jurisdictions. While India focuses on the DPDP Act, European operations must align with GDPR video personalization alignment. GDPR classifies the automated processing of personal data for marketing as “profiling,” which often requires a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) if the personalization is deemed high-risk.
Ad platforms like YouTube and Meta have standardized their disclosure requirements to align with these global regulations. YouTube, for instance, requires creators to check a disclosure box during the upload process if the content features realistic altered or synthetic media. Failure to do so can lead to the platform applying a label automatically—or worse, removing the content for policy violations.
The operational checklist for ad platform compliance includes:
- Ensuring the “AI-generated” disclosure is visible in the first five seconds of the video.
- Including a link to the Content Credentials in the video description or ad metadata.
- Verifying that the landing page associated with the ad also carries consistent transparency signals.
- Maintaining a “Provenance Pack” for each campaign, containing the C2PA manifest and a record of talent consent, to be produced upon platform request.
Source: YouTube AI Content Measures
Source: Meta AI Labeling Policies
5. Risk Mitigation: Deepfake Detection Protocols and Brand Safety
To maintain brand safety AI watermarking, enterprises must implement deepfake detection protocols both before and after content distribution. Pre-publish controls involve running forensic scans on all synthetic outputs to ensure they do not inadvertently trigger platform “harmful content” filters. This includes verifying that the C2PA manifest is correctly signed and that the invisible watermark is robust enough to survive the compression algorithms of WhatsApp or Instagram.
Post-publish monitoring is equally vital. Enterprises should utilize watermark search tools to track where their synthetic assets are being re-uploaded or potentially manipulated. If a competitor or bad actor attempts to “deepfake the deepfake” by altering a brand’s authorized synthetic video, the original watermark and C2PA manifest serve as the definitive proof of the authentic version.
Furthermore, integrating with third-party trust labs provides an additional layer of verified content certification. These labs can validate that a brand's watermarking implementation meets industry benchmarks for detectability and robustness. This proactive stance not only reduces the risk of accidental policy violations but also builds significant trust with savvy consumers who are increasingly skeptical of unverified digital media.
Source: Deloitte GenAI Trust Standards
Source: OpenAI Sora Watermarking Trends
6. Implementation Blueprint: Operationalizing C2PA Watermarking AI Video Marketing
TrueFan AI's 175+ language support and Personalised Celebrity Videos provide the ideal foundation for a compliant, high-scale video strategy. Implementing a reference architecture for C2PA watermarking AI video marketing involves a multi-step workflow that prioritizes transparency and data integrity.
First, the intake process must capture DPDP-compliant consent tokens. These tokens are pushed to the rendering API, ensuring that no video is generated without a verified legal basis. During the generation phase, the pipeline embeds the C2PA manifest and an invisible watermark into each personalized variant. For a campaign like Hero MotoCorp’s 2.4 million greetings, this means 2.4 million unique, cryptographically signed assets are produced, each carrying its own provenance record.
Second, the storage and distribution layer must preserve these signals. Assets are stored in a Digital Asset Management (DAM) system with hash indexes that link back to the original consent record. When exported to ad platforms or messaging apps, the system automatically appends the required disclosure text. Solutions like TrueFan AI demonstrate ROI through this seamless integration of compliance and creativity, allowing brands to focus on engagement while the platform handles the complexities of AI transparency requirements.
Finally, the governance framework must include a quarterly audit of all provenance controls. This involves testing the detectability of watermarks across different channels and ensuring that the C2PA manifests remain valid. By maintaining this level of operational rigor, enterprises can confidently scale their AI video initiatives, knowing they are fully aligned with the global standards of 2026.
7. Conclusion: The Future of AI Overviews Trust Signals Video
As search engines and social feeds transition toward AI-driven discovery, the importance of AI Overviews trust signals video cannot be overstated. Search algorithms in 2026 will prioritize content that carries verified provenance, as it represents a lower risk of spreading misinformation. By embedding C2PA manifests and maintaining accurate schema.org metadata, brands can ensure their video content is recognized as “authoritative” by both Google and Meta.
The transition to a fully transparent AI video ecosystem is not merely a regulatory burden; it is a competitive advantage. Brands that lead with verified content certification will earn the trust of a skeptical public and the favor of platform algorithms. The roadmap is clear: integrate consent, automate provenance, and verify every frame.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between C2PA manifests and digital watermarking?
C2PA manifests are cryptographic metadata files (Content Credentials) that provide a detailed history of an asset's creation and edits. Digital watermarking involves embedding a signal directly into the video's pixels or audio. While manifests can be stripped during certain types of file conversion, robust watermarks are designed to persist through re-compression and editing, providing a secondary layer of provenance.
How does the India DPDP Act specifically affect personalized AI video marketing?
The DPDP Act requires that any personal data used to create a personalized video (like a name or image) must be processed based on explicit, informed consent. Brands must provide a clear notice, maintain records of consent, and offer a simple way for users to withdraw that consent. If consent is withdrawn, the brand must ensure that the specific personalized asset is no longer used or rendered.
Are platforms like YouTube and Meta capable of reading C2PA credentials?
Yes, by 2026, most major platforms have integrated C2PA-aware ingestion pipelines. When a video with a valid C2PA manifest is uploaded, these platforms can automatically display a “Content Credentials” icon (often a “CR” badge), which allows viewers to see the provenance information directly within the platform's user interface.
Can TrueFan AI help our organization meet these 2026 compliance standards?
TrueFan AI is designed with an enterprise-first approach to compliance. By utilizing TrueFan AI, organizations can automate the inclusion of C2PA manifests and watermarking within their personalized video pipelines, ensuring that every asset generated is compliant with both Indian and global transparency mandates.
What happens if an enterprise fails to label synthetic media in India?
Under the current MeitY advisories and the proposed 2025 amendments, failure to label synthetic media can result in significant penalties, including the loss of “safe harbor” protection for intermediaries and potential legal action for deceptive practices. Additionally, ad platforms may shadow-ban or remove unlabeled AI content to protect their own compliance standing.




