Voice commerce regional languages India 2026: A practical roadmap for Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, and Tier-2 markets
Key Takeaways
- By 2026, vernacular voice commerce will dominate India’s digital retail, led by Tier-2/3 users
- Code-switching (Hinglish, Tanglish, Benglish) and dialect handling are critical for ASR/NLU success
- Deploy language-specific playbooks for Hindi, Bengali, and Tamil to boost discovery and conversions
- Track voice-originated ROI with KPIs like enablement rate, AOV uplift, and offer redemption
- Scale adoption via multilingual automation and trust-building with voice-verified payments
The landscape of digital retail is undergoing a seismic shift as voice commerce regional languages India 2026 becomes the definitive frontier for brand growth. By 2026, India is projected to have over 650 million vernacular internet users, with nearly 75% of all web interactions expected to be voice-led or voice-assisted. This transition is not merely a technological upgrade but a fundamental behavioral pivot where 7 out of 10 online shoppers now hail from Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities, demanding interfaces that speak their language, literally and figuratively.
As we approach this tipping point, the convergence of improved Indic-language Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), the ubiquity of smart speakers, and the rollout of conversational payment systems like Hello! UPI is creating a multi-billion-dollar opportunity. For technology leaders and regional marketers, the challenge lies in moving beyond simple translation to deep linguistic and cultural resonance. This roadmap provides a strategic framework for mastering voice commerce in Hindi, Bengali, and Tamil, ensuring your brand is ready for the vernacular-first era of 2026.
Why 2026 is India’s Tipping Point for Voice Commerce
The year 2026 represents a perfect storm of infrastructure readiness, consumer maturity, and technological advancement. According to a 2026 Mordor Intelligence report, the voice recognition market in India is growing at a staggering CAGR of 22.38%, projected to reach a valuation of $22.49 billion by the end of the year. This growth is fueled by a massive influx of first-time internet users who bypass the keyboard entirely, preferring the intuitive nature of voice commands to navigate complex e-commerce catalogs.
Infrastructure has finally caught up with ambition. The India smart speaker market has seen a consistent double-digit growth rate, transitioning from a niche luxury to a household utility in urban and semi-urban settings. Simultaneously, the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has revolutionized the checkout experience with “Hello! UPI,” an AI-voice-enabled payment feature that allows users to complete transactions via simple voice prompts. This removes the final friction point in the voice-to-purchase funnel, making conversational commerce a reality for millions.
Furthermore, the demographic shift is undeniable. Research from Bain & Company indicates that Tier-2+ shoppers now comprise the majority of the online shopping population. These users are not just browsing; they are transacting in regional languages. NASSCOM reports that 28% of all searches in India are already voice-based, with a significant portion occurring in Hindi, Bengali, and Tamil. For brands, ignoring this segment means forfeiting the fastest-growing consumer base in the world.
Source: Mordor Intelligence: Voice Recognition Market Growth 2026
Source: Bain & Company: How India Shops Online
Source: NPCI: Hello! UPI Product Overview
Source: NASSCOM: Voice Commerce Readiness
Regional Voice Shopping Behavior: Decoding Hindi, Bengali, and Tamil Nuances
Understanding regional voice shopping behavior requires a departure from standard UX principles. Vernacular users do not interact with assistants in the same way English-speaking users do. Their queries are often longer, more conversational, and heavily influenced by local shopping cultures—mimicking the back-and-forth dialogue one might have with a local shopkeeper.
One of the most critical patterns to design for is “code-switching.” In India, language is rarely monolithic. A Hindi speaker might say, “Mujhe sasta pressure cooker dikhaiye,” while a Tamil speaker might ask, “Offer enna irukku for two tickets?” These mixed-language utterances (Hinglish, Tanglish, Benglish) are the norm, not the exception. Your Natural Language Understanding (NLU) models must be trained on these hybrid datasets to avoid high abandonment rates.
Trust and confirmation are also paramount. In Tier-2 and Tier-3 markets, users often require verbal reassurance at every step of the journey. They prefer hearing the total amount, the applied discount, and the expected delivery date read back to them before confirming a payment. This “shopkeeper-style” interaction builds the necessary trust for high-value transactions. Additionally, dialectical variations—such as the difference between Kolkata Bengali and the dialects spoken in North Bengal—can affect entity recognition, requiring a more granular approach to ASR tuning.
Key Behavioral Drivers in 2026:
- Bargaining Tone: Users often ask for “best price” or “extra discount” even if the price is fixed.
- Literacy Bridge: Voice acts as a bridge for users who may struggle with complex app navigation or typing in native scripts.
- Audio Confirmation: A preference for voice-based OTPs and payment success announcements.
Source: Gnani.ai: Voice AI in Tier-2 Cities
Source: Outlook Business: India's Vernacular LLM Scramble
Language-Specific Implementation Playbooks: Hindi, Bengali, and Tamil
To succeed in voice commerce regional languages India 2026, brands must deploy specialized playbooks for the three dominant linguistic clusters. Each language presents unique challenges in terms of morphology, syntax, and search intent.
Hindi Voice Search Marketing
Hindi is the primary driver of voice adoption in India. Hindi voice search marketing involves optimizing your product catalog for question-led queries. Users typically use “kya” (what), “kaise” (how), and “kahan” (where) to discover products. For instance, a query like “Mere liye ₹500 ke neeche sports shoes dikhao” (Show me sports shoes under ₹500) requires an NLU that can extract both the category and the price constraint accurately. Brands should implement “speakable” schema markup and create FAQ sections in Hindi transliteration to capture these long-tail voice queries.
Bengali Voice Shopping Optimization
Bengali voice shopping optimization requires a deep understanding of regional unit measures and dialectical nuances. Bengali speakers often use specific terms for quantities (e.g., “ek palla” or “ek kg”) that must be mapped to your inventory system. Sample utterances like “Kom dame good quality rice ache?” (Is there good quality rice at a low price?) demonstrate a need for sentiment-aware search. Your system should be able to read back price totals and offers in a neutral, clear Bengali accent to maintain professional trust.
Tamil Conversational Commerce AI
Tamil is characterized by its high morphological complexity and distinct formal vs. informal registers. Tamil conversational commerce AI must be tuned for “Tanglish” commands and graceful agent handoffs. A user might say, “₹1000-kku keezhe best mixer grinder kaamikka” (Show the best mixer grinder under ₹1000). The NLU must handle the suffix-heavy nature of Tamil words while identifying the brand and price intent. Providing brief, multiple-choice readouts for variations (size, color, brand) is more effective than long, descriptive lists in Tamil voice flows.
Source: TrueFan AI: Regional Language Voice Shopping Trends
Source: IMARC Group: India Voice Recognition Market
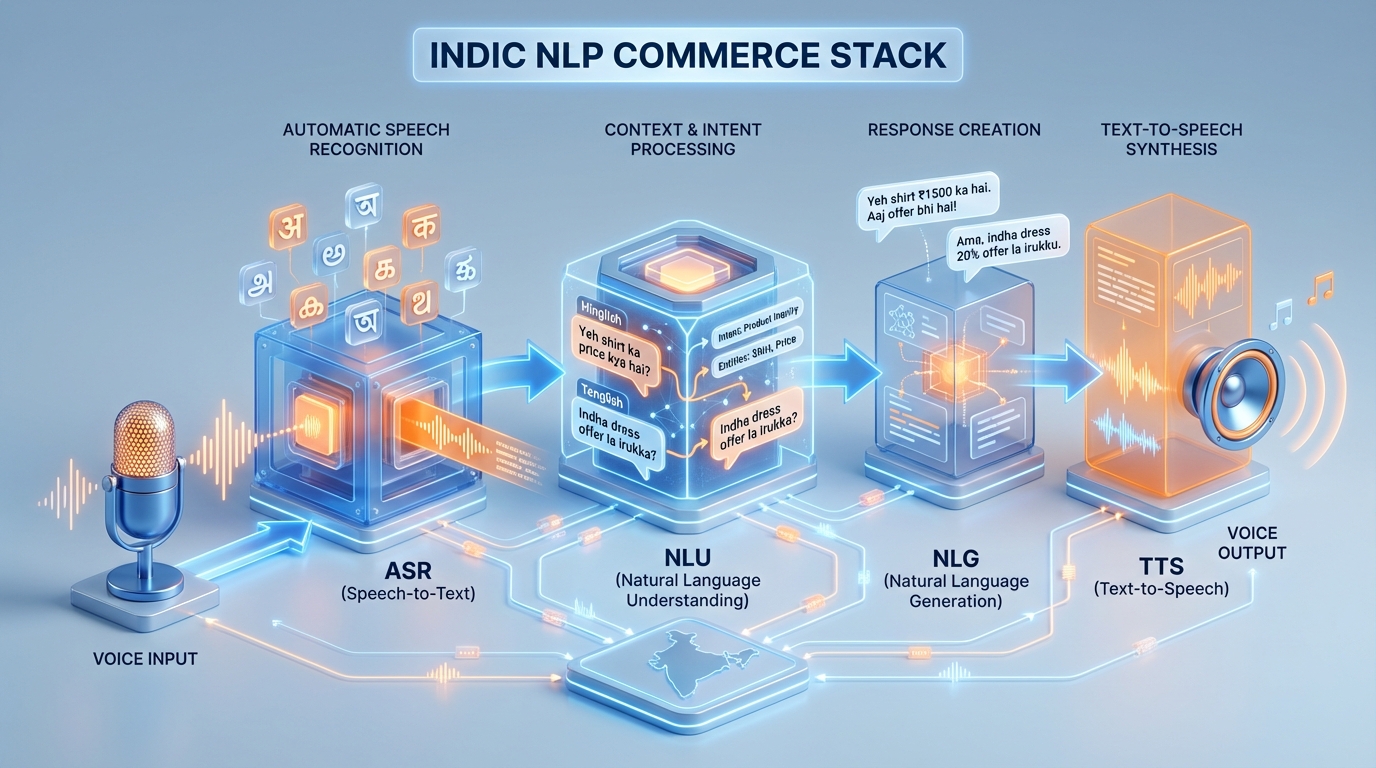
The Natural Language Processing Commerce Stack for Indic Languages
A robust natural language processing commerce stack is the engine behind successful voice integration. By 2026, the standard for “Indic-ready” stacks has moved beyond generic APIs to specialized pipelines that handle noise robustness, code-switching, and regional prosody.
The stack begins with ASR (Speech-to-Text), which must be resilient to the varied acoustic environments of India—from noisy streets to crowded households. Following this, the NLU (Natural Language Understanding) layer extracts intent and entities. In the Indian context, this means recognizing product attributes like “pure silk” or “100% cotton” in multiple languages simultaneously. The NLG (Natural Language Generation) layer then crafts a response that is concise and “speakable,” avoiding the robotic tone of early-generation assistants.
Finally, the TTS (Text-to-Speech) component must offer neutral regional voices that sound human and empathetic. For 2026, the integration of vernacular voice assistant integration across surfaces like Google Assistant, Alexa, and in-app voice is mandatory. This includes account linking and consent management in the user’s local language. Technical leaders must also ensure that their stack includes guardrails for PII (Personally Identifiable Information) redaction and compliance logging, especially as voice data falls under stricter privacy regulations in 2026.
Essential Stack Components:
- Indic ASR: Tuned for 22+ official languages and 100+ dialects.
- Code-Switched NLU: Capable of processing Hinglish, Tanglish, and Benglish.
- Dynamic TTS: Real-time synthesis of prices, dates, and names with correct regional intonation.
- Contextual Memory: Remembering previous voice interactions to provide a seamless “shopping assistant” experience.
Source: Future Market Insights: Voice Commerce Services Market
Source: IMARC Group: India Smart Speaker Market
Voice-Activated Offer Redemption and ROI Measurement
One of the most potent tools for driving conversion in 2026 is voice-activated offer redemption. This allows users to discover, verify, and apply discounts entirely through voice commands, significantly reducing the “cart abandonment” that often occurs during manual coupon entry. A typical flow might involve a user saying, “Apply my 10% discount,” followed by a voice-PIN or OTP verification, and a verbal confirmation that the price has been updated.
However, implementing these features requires a rigorous approach to voice commerce ROI measurement. Brands must move beyond vanity metrics like “number of voice sessions” to track incremental financial impact. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for 2026 include:
- Assistant Enablement Rate: The percentage of users who opt-in to voice features.
- Voice-Originated Conversion Rate: Comparing voice-led journeys against traditional app-based journeys.
- Average Order Value (AOV) Uplift: Measuring if voice-assisted discovery leads to higher-value carts.
- Redemption Rate: The success of voice-activated offers vs. typed codes.
Solutions like TrueFan AI demonstrate ROI through their ability to bridge the gap between voice discovery and visual engagement. By delivering personalized video explainers in the user’s language immediately after a voice interaction, brands can see a significant lift in repeat purchase rates and customer lifetime value (CLV). Measuring these cross-channel assisted conversions is critical for justifying the investment in a multilingual voice strategy.
Source: NPCI: Hello! UPI Brand Guidelines
Source: NPCI: UPI 123PAY for Feature Phones
Tier-2 Voice Commerce Adoption: Scaling with Multilingual Marketing Automation
The ultimate success of your 2026 strategy hinges on tier-2 voice commerce adoption. In these markets, voice is not just a convenience; it is a primary mode of digital inclusion. To scale effectively, brands must employ multilingual voice marketing automation that orchestrates journeys across Hindi, Bengali, and Tamil based on user behavior and location.

Platforms like TrueFan AI enable brands to educate this new wave of shoppers through hyper-personalized content. For example, when a user in Kanpur enables the Hindi voice assistant, they can receive a personalized video from a celebrity like Kareena Kapoor Khan, explaining in Hindi how to use voice commands to find the best deals. This high-touch approach builds trust and lowers the barrier to entry for non-tech-savvy users.
TrueFan AI’s 175+ language support and Personalised Celebrity Videos allow for the rapid creation of localized “How-To” guides and festival-specific offer announcements. Instead of generic ads, a user in Coimbatore might see a video in Tamil from a regional star, encouraging them to try the “voice-activated offer redemption” feature during Pongal. This level of conversational AI personalization ensures that the brand remains relevant across India’s diverse cultural landscape.
Phased Execution for Tier-2 Markets:
- Education: Use personalized videos to teach voice navigation.
- Activation: Trigger voice-only offers via WhatsApp and SMS.
- Retention: Use voice-based loyalty updates and re-engagement nudges.
- Trust: Implement Hello! UPI for secure, voice-verified payments.
Conclusion: The Roadmap to 2026
The transition to voice commerce regional languages India 2026 is an inevitable evolution of the Indian digital economy. By focusing on the specific linguistic needs of Hindi, Bengali, and Tamil users, and leveraging the growth of Tier-2 markets, brands can unlock unprecedented levels of engagement and loyalty.
Success in this era requires a holistic approach: a robust NLP stack, a deep understanding of regional shopping behaviors, and the strategic use of automation and personalization. As voice becomes the primary interface for the “Next Billion Users,” the brands that speak their language today will be the market leaders of tomorrow. The roadmap is clear—now is the time to build the voice-first future of Indian retail.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I enable voice shopping in Hindi for my e-commerce app?
To enable voice shopping in Hindi, you must integrate an Indic-ready ASR and NLU stack. Start by mapping your product catalog to Hindi keywords and transliterations. Ensure you use Hindi voice search marketing strategies like implementing “speakable” schema and creating FAQ sections that answer common queries like “Sasta saman dikhao” (Show cheap items). Platforms like TrueFan AI can help by providing personalized video tutorials in Hindi to guide your users through the setup process.
Is Hello! UPI safe for voice-activated payments?
Yes, Hello! UPI is designed with multiple layers of security. It uses AI-voice recognition to verify the user’s intent and requires a second factor of authentication, such as a voice-PIN or a traditional OTP, to complete the transaction. The system also reads back the final amount and recipient name in the user’s regional language (Hindi, Bengali, or Tamil) to ensure transparency and prevent fraud.
How does Bengali voice shopping optimization differ from English?
Bengali voice shopping optimization focuses on the unique syntax and honorifics used in the Bengali language. Unlike English, which is relatively direct, Bengali queries are often more descriptive and may include regional unit measures. Your NLU must be trained on specific Bengali dialects (e.g., Dhakai vs. Ghoti) to accurately recognize product names and quantities.
What are the key KPIs for measuring voice commerce ROI in 2026?
The primary KPIs include the Voice Conversion Rate (CVR), Average Order Value (AOV) for voice-assisted sessions, and the Voice-Activated Offer Redemption rate. Additionally, brands should track the “Enablement Rate” to see how many users are successfully transitioning from touch to voice interfaces in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities.
Can I use Tamil conversational commerce AI for customer support?
Absolutely. Tamil conversational commerce AI is highly effective for handling routine support queries like order tracking, return requests, and offer inquiries. By using a system that understands “Tanglish” and Tamil morphology, you can resolve up to 70% of customer queries without human intervention, significantly reducing operational costs while improving user satisfaction in the Tamil-speaking market.




