Voice commerce vernacular India 2026: An enterprise blueprint to win Hindi, Tamil, Bengali shopping across tier-2/3
Estimated reading time: 11 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Vernacular voice commerce in Hindi, Tamil, and Bengali unlocks tier-2/3 penetration by reducing typing friction and cognitive load.
- Bhashini and advances in ASR/TTS enable dialect-aware, low-error natural language commerce across devices.
- An end-to-end conversational shopping AI stack (ASR, NLU, policy engine, UPI flow) is essential for secure, scalable transactions.
- Smart speaker integration and multilingual marketing automation increase retention via geo-targeted, voice-led reorders.
- A 90–180 day enterprise roadmap with pilots and scale plans drives measurable ROI with analytics and governance.
“Voice commerce vernacular India 2026” will be decisive for Digital Innovation Teams and Regional Expansion Leaders aiming to capture India’s vernacular growth in Hindi, Tamil, and Bengali via conversational shopping AI, smart speaker commerce integration, and multilingual voice marketing automation. This blueprint provides a practical 90–180 day roadmap, enterprise architecture, and ROI framework to activate tier-2 voice shopping adoption and voice-activated personalized offers at scale.
The 2026 opportunity: Why regional language voice shopping leads tier-2/3 penetration
“Regional language voice shopping” is the end-to-end shopping journey triggered, navigated, and completed through speech in local languages such as Hindi, Tamil, and Bengali. By operating across mobile apps, voice assistants, and smart speakers, this technology reduces typing friction and cognitive load for non-English users, effectively democratizing digital commerce.
The market signals for 2026 are undeniable. According to the IAMAI–Kantar "Internet in India 2024" report, rural areas are leading internet usage growth, putting India on track for 900 million internet users by 2025, with a deepening reliance on non-English interfaces. Furthermore, IndiaMART’s corporate data reveals that 98% of internet users accessed local-language content in 2024, signaling that voice and vernacular are the primary engines of the next digital wave.
By 2026, the baseline milestone for 540 million vernacular users targeting will expand toward 650 million users. This shift is not merely rural; urban multilingual behavior is also evolving, with 82% of Indians now preferring AI-driven recommendations. As social commerce demand moves beyond Tier I cities, platforms are seeing a surge in WhatsApp and voice-led experiences that cater to the unique linguistic nuances of the "Next Billion Users."
Sources:
- IAMAI–Kantar Internet in India 2024 Report
- IndiaMART: Talking Tech—Voice and Vernacular
- MXM India: India’s Digital Surge in 2026
- LS Digital: The Rise of AI-Native Advertising in India
- Ginesys: Top Social Ecommerce Platforms India 2025
Policy and infrastructure enablers powering natural language commerce India
“Natural language commerce India” refers to transaction workflows—including browsing, applying offers, checkout, and customer service—executed through speech in Indian languages using NLU (Natural Language Understanding) and ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) tuned to specific dialects. This movement is heavily supported by the government’s National Language Translation Mission, known as Bhashini.
Bhashini’s mission is to bridge digital, literacy, and language divides by enabling voice-first multilingual access to essential services. For enterprise leaders, this means that improvements in Indic ASR and Text-to-Speech (TTS) are significantly lowering word-error rates, allowing for dialect-aware experiences that were previously impossible.
Building atop Bhashini-compatible architectures improves recognition for Hindi, Tamil, and Bengali queries even in noisy environments or on low-end devices. This infrastructure is critical for capturing vernacular long-tail keywords and ensuring that voice assistant regional marketing remains accurate across diverse geographical clusters.
Sources:
User behavior and language priorities: Hindi, Tamil, and Bengali voice design
Hindi voice search optimization playbook
Hindi voice search optimization involves tuning content, metadata, and NLU engines to the natural speech patterns of Hindi speakers, which often include code-mixing (Hinglish), colloquialisms, and Hindi numerals. Enterprise teams must move beyond literal translation to capture intent-rich phrases.
For example, a user might ask, “10,000 ke andar sasta smartphone” (Cheap smartphone under 10,000) or “Noida mein behtareen running shoes kahan milenge?” (Where can I find the best running shoes in Noida?). Capturing these variations requires implementing Speakable and HowTo structured data that maps directly to product facets like brand, price, and delivery availability.
Tamil voice commerce campaigns architecture
Tamil voice commerce campaigns are defined by language-and-dialect-tuned offers that respect regional variations such as Kongu Tamil, Madurai Tamil, and Chennai colloquialisms. A user in Coimbatore might ask, “Salem-la same-day delivery irukka?” (Is same-day delivery available in Salem?).
Effective architecture for Tamil voice requires synonym lists and phonetic spellings to handle the complexity of the script and its spoken variants. Designing fallback confirmations, such as “Neenga [product] thedureengala?” (Are you looking for [product]?), ensures the conversational shopping AI maintains high accuracy during the transaction flow.
Bengali conversational AI marketing flows
Bengali conversational AI marketing focuses on intent-led, voice-initiated journeys using colloquial Bengali and regional variations like Sylheti or Rarhi. Common queries include “koto din’er warranty?” (How many days of warranty?) and “COD ache?” (Is COD available?).
Enterprises should use disambiguation prompts for units and prices while confirming addresses in Bengali to build trust. Leveraging localized holidays like Poila Baisakh for offer timing can significantly increase the relevance of voice-activated personalized offers in the West Bengal and Tripura markets.
Sources:
Mining vernacular long-tail keywords and mapping to conversational intent
Vernacular long-tail keywords are multi-token, colloquial, and attribute-rich voice phrases that reflect how people actually speak rather than how they type. These keywords often include specific mentions of price, location, and assurance (e.g., “guarantee” or “return policy”).
The process of mining these keywords begins with harvesting data from internal search logs, WhatsApp voice note transcripts, and call-center queries. These are then clustered by intent: discovery, comparison, promotion, payment, or post-purchase. Marketers must normalize code-mixed forms, such as using both Devanagari and Latin scripts for Hindi, to ensure comprehensive coverage.
By 2026, the dominance of vernacular content will require brands to publish dedicated content hubs with Q&A sections in regional languages. Implementing Speakable and FAQ schema allows these long-tail intents to be picked up by voice assistants, creating a seamless bridge between natural language commerce India and the final purchase.
Sources:
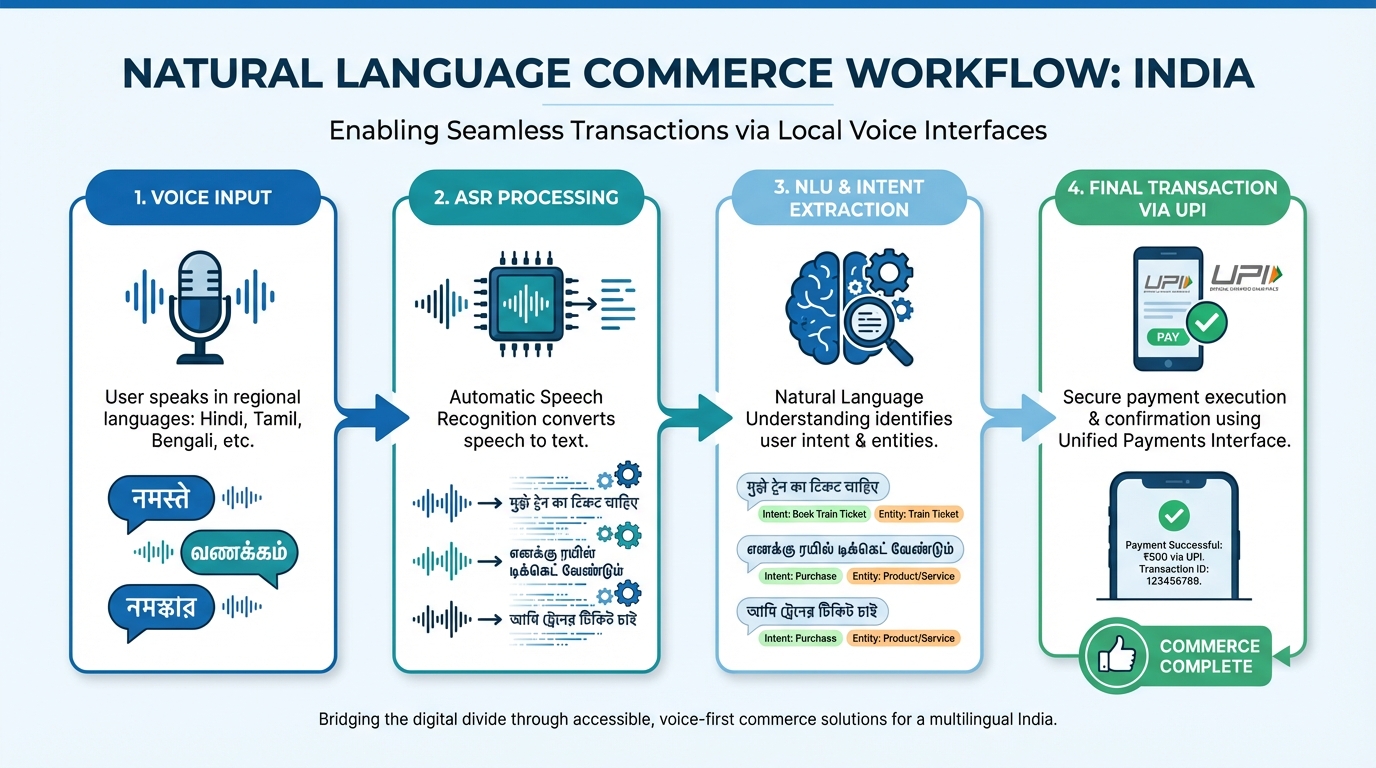
Conversational shopping AI architecture: From intent to transaction
Conversational shopping AI is an orchestration of several technical layers: ASR for speech-to-text, NLU for intent and entity extraction, a policy engine for offers, catalog search, and a payment gateway integrated with UPI. For the Indian market, this stack must be optimized for low-signal-to-noise (SNR) environments typical of tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Key design principles include creating an intent taxonomy that shares a common backbone across languages while maintaining specific entity models for brand, size, and locality. Error handling is paramount; the system should provide top-2 intent confirmations and use TTS prompts in the same dialect as the user to maintain conversational flow.
The final step in the architecture is the payment flow. In 2026, natural language commerce India will rely heavily on voice-confirmed UPI mandate flows. This involves a voice confirmation followed by a push request to the user’s UPI app, ensuring security through OTP obfuscation and explicit voice-based consent.
Sources:
Multilingual voice marketing automation and smart speaker integration
Multilingual voice marketing automation involves the cross-language orchestration of campaigns that trigger personalized voice or video offers based on real-time customer behavior. These triggers—such as a price drop or a reorder reminder—can be delivered via WhatsApp, mobile apps, or smart speakers.
Smart speaker commerce integration enables users to add items to their cart, reorder essentials, and track orders through Alexa or Google Assistant in their native language. A frictionless dialog might look like this: “Add two Surf Excel 1kg to cart,” followed by the assistant recapping the basket and confirming the MRP in Hindi or Tamil.
To succeed in voice assistant regional marketing, enterprises must use geo-targeted offers aligned with local festivals like Pongal or Durga Puja. Success is measured by the assistant invocation click-through rate (CTR) and the frequency of voice-led reorders, which typically show higher retention than traditional app-based journeys.
Sources:
Enterprise implementation with TrueFan AI: Scaling ROI in 2026
Scaling a voice-led commerce program requires a robust technical partner capable of handling the complexities of the Indian linguistic landscape. Platforms like TrueFan AI enable enterprises to bridge the gap between voice intent and high-conversion visual engagement through real-time APIs and low-latency rendering.

TrueFan AI's 175+ language support and Personalised Celebrity Videos allow brands to respond to a voice query with a hyper-personalized video message. For instance, after a user searches for a product via voice, they can receive a WhatsApp video featuring a celebrity speaking their name and dialect, restating the offer, and providing a direct link to checkout.
Solutions like TrueFan AI demonstrate ROI through comprehensive analytics dashboards that track watch-through rates, conversion lift, and cohort LTV by language and dialect. Furthermore, the platform’s adherence to ISO 27001 and SOC 2 standards ensures that all multilingual data handling and voice-activated personalized offers meet the highest enterprise security and governance requirements.
90–180 Day Roadmap to Scale
- Days 0–30 (Discovery): Identify high-value use cases like reorders or assisted discovery. Mine vernacular long-tail keywords and prototype Hindi voice flows.
- Days 31–90 (Pilot): Launch a Hindi pilot on WhatsApp. Integrate voice-activated personalized offers and measure the AOV (Average Order Value) uplift.
- Days 91–180 (Scale): Expand to Tamil and Bengali dialects. Implement smart speaker commerce integration and automate campaign operations using multilingual voice marketing automation.
Industry-Specific Recipes
- Retail/CPG: Use voice-led replenishment for household staples. Follow up a voice search with a personalized celebrity video coupon on WhatsApp to drive immediate conversion.
- BFSI: Implement voice-activated premium reminders and lead qualification. Use localized trust messaging in the user’s native dialect to improve KYC completion rates.
- Travel: Enable fare watchlists via voice. Send a voice-activated personalized video itinerary recap in Bengali or Tamil to enhance the post-booking experience.
Conclusion
Voice commerce vernacular India 2026 will define the next generation of market leaders in the Indian subcontinent. By moving beyond English-centric interfaces and embracing regional language voice shopping, brands can unlock unprecedented growth in tier-2 and tier-3 markets. The combination of conversational shopping AI and voice-activated personalized offers creates a high-trust, low-friction environment that resonates with the cultural and linguistic preferences of 650 million users.
To stay ahead, enterprises must act now to integrate smart speaker commerce integration and multilingual voice marketing automation into their core digital strategy. TrueFan AI offers the real-time APIs, multilingual localization, and enterprise-grade security needed to transform voice intent into measurable revenue.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do we approach dialect-specific voice campaigns at scale without high error rates?
Success requires using NLU models that are trained on regional datasets rather than standard translations. Implementing a “confirm-and-proceed” logic for high-value entities like price and quantity ensures that dialect variations do not lead to transaction errors.
What are best practices for Hindi voice search optimization for ecommerce?
Focus on Hinglish transliteration and capturing colloquial price-related queries. Use structured data to help search engines understand that your content is optimized for “Speakable” intents, particularly for product discovery in tier-2 cities.
What’s required for smart speaker commerce integration in Hindi, Tamil, and Bengali?
You need to develop custom skills or actions that support account linking and voice PINs for security. The UX must be designed for “eyes-free” interaction, where the assistant reads back the order summary and promo logic clearly in the local language.
How does TrueFan AI help in measuring the ROI of voice-led campaigns?
TrueFan AI provides detailed dashboards that stitch voice events to final purchases. By tracking conversion lift and customer lifetime value (LTV) across different language cohorts, enterprises can refine their multilingual voice marketing automation strategies for maximum impact.
How does natural language commerce in India address privacy and consent?
Enterprises must implement explicit consent prompts in the user's local language before recording any voice data. Data minimization policies and encryption are essential, ensuring that PII (Personally Identifiable Information) is handled according to ISO 27001 standards.




